Design a Queue Class Using a Vector to Store Data
Difference Between C++ Vector and Array
Vectors are sequence containers that utilize continuous storage locations to store elements. They can manage storage and grow dynamically in an efficient way. These abilities come at a price: vectors consume more memory in exchange to handle storage and grow dynamically in size. vector<int> v; where v is the variable of type Vector store integer elements.
Example of C++ Vector and Array
This is known as initialization of vector:
Store random integer with function "push_back":
v.push_back(11);
v.push_back(12);
v.push_back(13);
v.push_back(14);
Using function "pop_back()", to remove the last element:
v.pop_back();
To remove the first element, we can use function erase():
v.erase(v.begin());
First element access with function front();
v.front();
Last element access with function back();
v.back();
Declare an array in C++: An array stores a fixed-size sequential collection of elements of the same type. It is used to store a data collection, but the array can be considered a collection of variables of the same type stored at contiguous memory locations. All arrays consist of contiguous memory locations, with the lowest address corresponds to the first element and the highest address to the last element.
type array_name[array_size]; // Type is used to specify type of elements in array
Initializing an array :
double values[5] = {23.7, 32.1, 66.7, 11.1, 44.6};
C++ has multidimensional array:
Type name[size1][size2]…..[sizeN];
Initializing two-dimensional array:
int a[3][4] = { {0,1,2}, {4,5,6,7}, {8,9,10,11} };
Passing a pointer to an array by specifying array name without index:
void dummyFunction( int *param){
}
With index:
void dummyFunction( int param[]){
}
Head to Head Comparison Between C++ Vector and Array (Infographics)
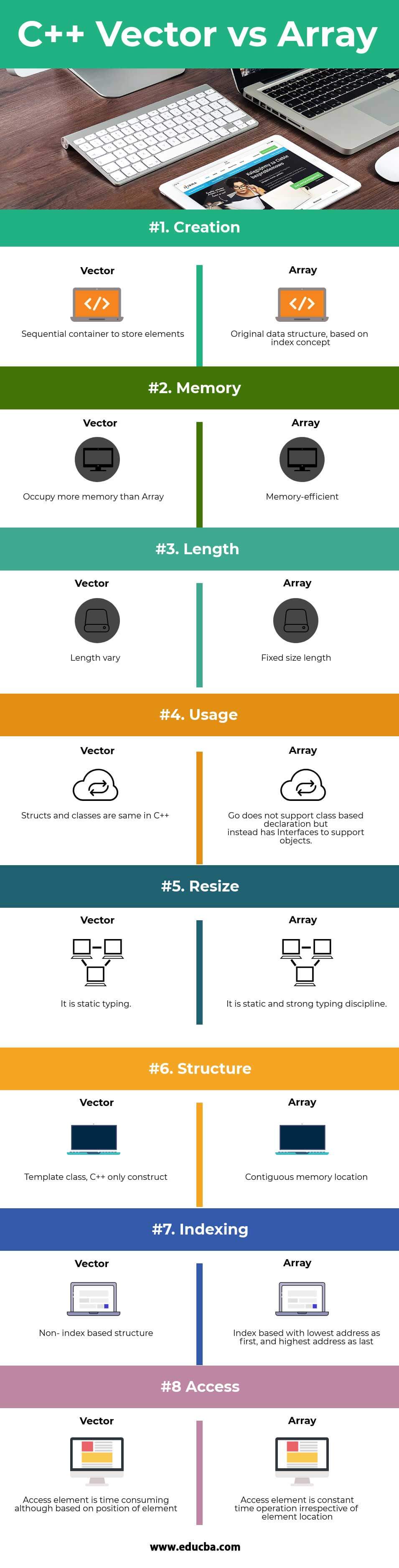
Below is the Top 8 difference between vector and array in c++
Key Difference between C++ Vector vs Array
Both C++ Vector vs Array are popular choices in the market; let us discuss some of the major difference between vector and array in c++:
- Vector are sequential containers, whereas Array is a lower-level data structure.
- Vector is shipped in the form of a template class in C++ with a parent as Collection class, whereas Array is the lower level data structure with its own specific properties.
- Vector is not index-based and having functions & constructors, whereas Arrays are index-based data structures with the lowest address is provided to the first element, and the highest address is provided to the last element in the array.
- Vector is dynamic in nature, i.e. their size automatically increases with more element insertion, whereas Arrays are the fixed-size structure, once initialized, cannot be reset.
- Vector is better for frequent insertion and deletion, whereas Arrays are much better suited for frequent access of elements scenario.
- Vector occupies much more memory in exchange for managing storage and growing dynamically, whereas Arrays are a memory-efficient data structure.
- Vector is derived from Collection, which contains a more generic data type, whereas Array is fixed and store a more strong data type.
- Vector store elements in a contiguous memory location and enable direct access to an element using subscript operator, whereas Array contains the elements with their memory location, which are contiguous in nature.
- Vector take more time in accessing the elements, whereas the contiguous property of Array makes them highly efficient for accessing the elements.
- Vector leverage generics, it is basically a type-safe version whereas Arrays, with its type-safe, highly efficient in terms of speed and performance, support multiple dimensions.
C++ Vector vs Array Comparison Table
Below is the topmost comparison
| The basis of comparison | Vector | Array |
| Creation | Sequential container to store elements | An original data structure, based on index concept |
| Memory | Occupy more memory than Array | Memory-efficient |
| Length | Length varies | Fixed-size length |
| Usage | Frequent insertion and deletion | Frequent element access |
| Resize | Resize Vector is dynamic in nature | Resizing arrays is expensive |
| Structure | Template class, C++ only construct | Contiguous memory location |
| Indexing | Non- index based structure | Index-based with the lowest address as first, and highest address as last |
| Access | Access element is time-consuming although based on the position of an element. | Access element is a constant time operation irrespective of element location. |
Conclusion
Both C++ Vector vs Array are distinct types, having different capabilities and store their data in separate ways. This storing capabilities and design of both C++ Vector vs Array data structures make them unique in their own ways. An Array is fixed in size, and once it is allocated, one cannot add or remove items from it; also, all elements must be of the same type. Thus, it is a type-safe and most efficient linear data structure in terms of speed and performance. Also, Array supports multiple dimensions. Vector is a template class, and C++ only construct. Unlike Array, they are dynamic in nature, can resize automatically with frequent insertion and deletion of elements. It is essentially a template class containing pointers into the heap, so when it always calls std: vector, "new" would always be called. Vector elements are guaranteed to be contiguous, but at the same time, they are slower for access because of the pointer-based approach. One needs to have access to a pointer first to get their hands-on data.
C++ Vector vs Array is a linear data structure that is well suited for different scenarios. If frequent insertion and deletion occur, and at the same time, memory is not a constraint, then Vector is an ideal choice, whereas in scenarios like frequent access of elements of required with a memory constraint, then Array is a better option. It all depends upon the use case and requirement. An array is always a list in nature, but a vector is a template class and same as a dynamic array. The array allows both kinds of access, direct and sequential, while Vector only allows sequential access. And this is because of the way these data structures are stored in memory. Since Vector elements are placed in a contiguous memory block, they can be easily traversed using an iterator.
There are multiple functions available in C++ with Vector as a template class, all functions are providing some sort of functionality around Vector i.e. begin(), end(), rbegin(), rend(), cbegin(), cend(), crbegin(), crend(), size(), max_size(), capacity(), resize(), empty(), reverse() and shrink_to_fit(). An Array is very much tied to the hardware notion of continuous, contiguous memory, with each element identical in size. Both C++ Vector vs Array ideas line up quite well, based on scenarios. At the end of the day, it all boils down to the requirement. A developer needs to weigh down the project requirement and thus make any decision.
Recommended Article
This has been a guide to the top differences between C++ Vector vs Array. Here we also discuss the key differences with infographics and comparison table. You may also have a look at the following C++ Vector vs Array articles to learn more –
- C++ reference vs pointer
- C# Array vs List
- C vs C++ Performance
- Java List vs Array List
- Require vs Import: What are the Benefits
- C vs C#: What are the Features
- C vs C++ | Top 13 Differences
- Complete Guide to C++ Reference
Design a Queue Class Using a Vector to Store Data
Source: https://www.educba.com/c-plus-plus-vector-vs-array/
0 Response to "Design a Queue Class Using a Vector to Store Data"
Post a Comment